This edition of Art Terms will focus on the various techniques and terminology in printmaking. The AGGV has substantial holdings of prints from North America, Europe and Asia.
1. Aquatint
This printmaking technique produced tonal effects, using acid to eat into the printing plate to create sunken areas in which ink is applied. Aquatint is an intaglio method (i.e. the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or area holds the ink) that creates tonal effects, rather than lines. The technique was first developed in France in the 1760s. It is often used in combination with other intaglio techniques.

2. Drypoint
Another intaglio technique, drypoint consists of a process where a design is incised onto a soft metal plate, such as copper. The process of incising on the soft metal creates a slightly raised ragged edge called the burr. Ink is applied and then wiped off, but the ink is caught in the incisions and the burr, thus creating the image. Drypoint prints are made in smaller runs, as the burr will be worn down with each press.
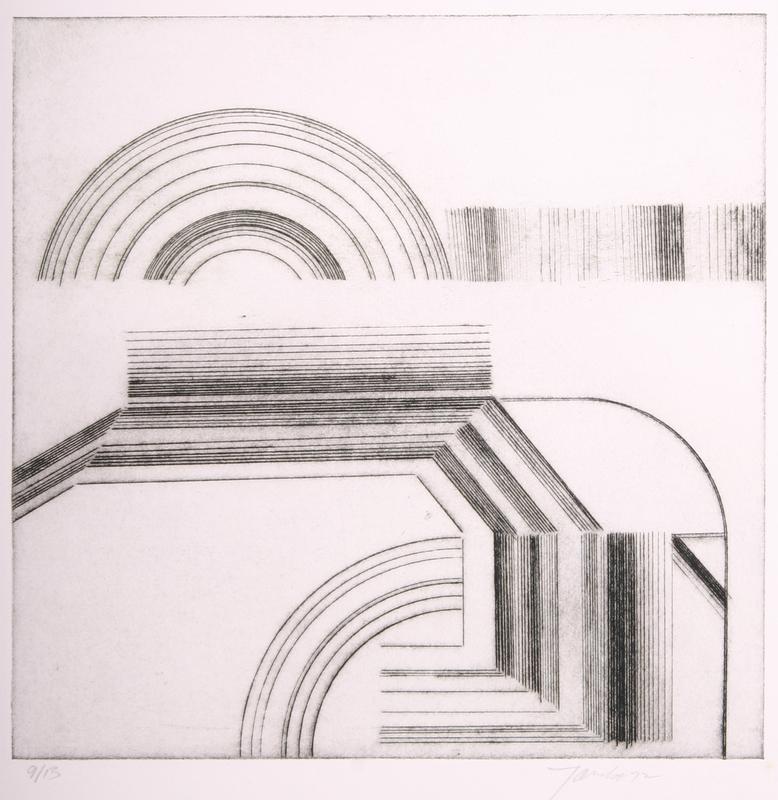
3. Etching
Similar to an aquatint, etching is another technique using a chemical reaction. A copper or zinc plate is prepared with an acid-resistant coating. Lines are incised through the ground to expose the metal base. The plate is then immersed into an acid bath, where the exposed metal lines are “eaten”, producing the lines of the design. The resist is removed and ink is applied to the sunken lines. The surface is wiped of excess ink – although sometimes, some remnants are left to provide background tone – and pressed onto paper. Etching is also an intaglio technique.
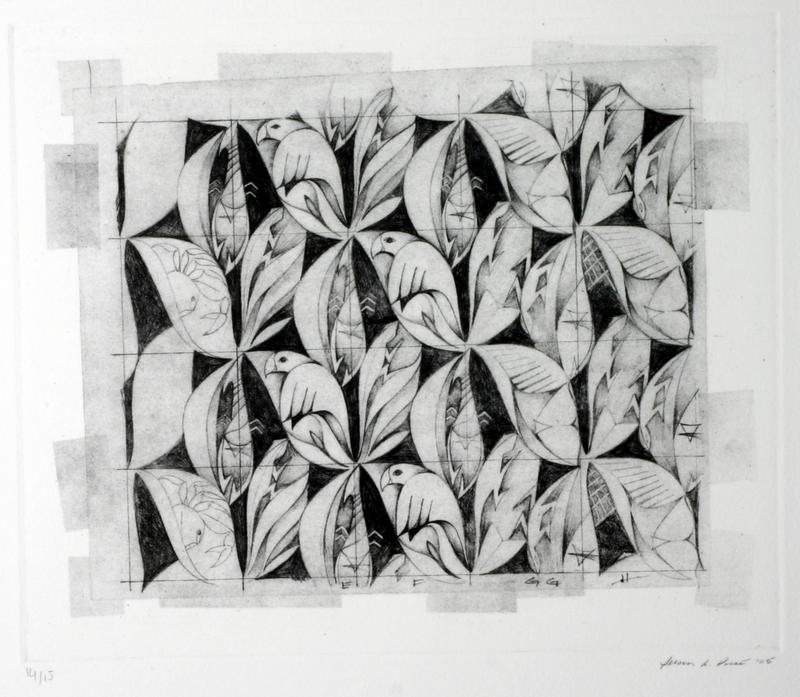

4. Lithograph
This printing technique uses a flat stone or metal plate, with the design worked in with a greasy substance to which the ink will adhere, while the other areas are made ink-repellent. The technique relies on the fact that oil and water don’t mix.

5. Monotype
A monotype is a unique image printed from a polished glass or metal plate which has been painted or inked with a design. The image is transferred when pressed onto paper. The plate may also be fully inked and the design is created by brushing away the ink to create lighter areas.

6. Registration
Registration refers to the precision and alignment of the print, meaning that the impression on the paper is made exactly as intended.